

- Home
- Flower Care 101
Flower Care 101
Common Flower Pests and Diseases

Aphids
Oval-shaped and small, typically less than 1/8 inch long; range in color from bright orange or red to dull gray; may or may not have wings. • Attack almost all types of roses and flowers, sucking juices from shoots, buds or leaves, causing them to curl. May impact the quality or number of blooms. Large infestations reduce plant growth and vigor. • Most aphids excrete large quantities of honeydew, a sweet, sticky substance that attracts wasps, ants and bees and can serve as a medium on which sooty mold can grow. Related: Scales, Whiteflies

Scales
Divided into two groups: armored and soft. • Armored scales are less than 1/8 in diameter and have a waxy covering that is separate from the insect body. Soft scales are less than 1/4 inch in diameter and have a waxy layer that is part of the insect body. Both types suck the juices from plants. • Feeding may reduce growth and may cause premature leaf drop. • Soft scales excrete honeydew, a sweet, sticky substance that attracts wasps, ants and bees and can serve as a medium on which sooty mold can grow. Related: Aphids, Whiteflies, Mealybugs

Leafminers
Small larvae of insects such as various flies, sawflies, small moths and beetles. • Feed on leaves by tunneling between the upper and lower leaf surfaces. Feeding damage leaves patterns on the leaf. Related: Sawflies

Roseslugs
Larvae are yellow-green and translucent, exposing a dark-green digestive track, with yellow to orange heads. Mature larvae are 1/2 inch long. • Feed on lower surfaces of rose leaves, skeletonizing leaves. Related: Sawflies

Japanese Beetles, Adult
Oval, 1/2 inch long, metallic green with copper-colored wings. • Feed on leaves of hundreds of plants, including roses. Feeding results in skeletonizing of leaves, making them appear lacelike. Related: Beetles
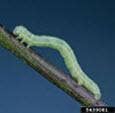
Caterpillars
Larvae of moths or butterflies. • Feed on the foliage or flowers of roses, resulting in oblong holes in leaves and buds or defoliation of the plants.

Thrips
Tiny, 1/16 inch long, slender sucking insects that are usually yellow, brown or black. • Prefer light-colored blooms in shades such as pale yellow, white or light pink. • Cause distorted or unopened buds, ragged and brown petal edges, and brown streaks on petals. Some thrips may also vector plant viruses.

Spider Mites
Tiny arachnids, 1/70 to 1/50 inch long. • Suck juices from plants and produce honeydew, which attracts ants and may host black sooty mold. • Leave silver stipples or spots on leaves and produce webbing on leaf undersides and between leaves and stems. May cause leaves to appear dull, stunted or discolored, as well as leaf drop. Related: Mites
Related products

Whiteflies
Tiny, white, fly-like insects that usually congregate on undersides of leaves. Often swarm in clouds when disturbed. • Suck juices from plants, leading to wilting and stunted growth. Severe infestations cause leaf yellowing and leaf drop. Whiteflies also excrete honeydew, a sweet, sticky substance that attracts wasps, ants and bees and can serve as a medium on which sooty mold can grow. Related: Aphids, Scales

Powdery Mildew
Fungal growth on surface of leaves and buds. • White and powdery. • May cause leaf deformity or curling.

Rust
Fungi. • Causes leaf drop and brown, orange or yellow leaf-spotting.

Foliar Fungal Diseases
Includes leaf spot and anthracnose, which cause brown, black or tan spots on leaves. Angular spots around veins often indicate anthracnose. Lead to yellowing and leaf drop. • Caused by fungi. • Often appear on trees that also have cankers.

Sooty Mold
Fungi. • This black-colored, threadlike fungus grows in honeydew secretions. • Coats the top sides of leaves, interfering with photosynthesis by blocking sunlight. Can lead to stunted growth and premature leaf drop.

Downy Mildew
Gray to brown fungus that develops on undersides of leaves. • Leads to foliage blights and distortion, mottled leaves, and leaf yellowing.

Petal Blight
Fungi. • Causes small, pale spots on colored petals and brown spots on white petals. Leads to brown, slime-covered flowers, petal drooping, and black, egg-shaped fungal masses visible on petals.

Bark Beetles
Vary in appearance. • Attack trees that are weakened, stressed or in decline. Attacks can be recognized by presence of brown boring dust, pitch tubes on the outside of the bark, galleries under the bark, beetle adults and larvae in the inner bark, tiny holes in branches and trunk, and yellowing or reddening tree crowns • Can transmit fungi that cause disease, such as Dutch elm disease.

Rose Stem Canker
Dead areas on rose stems that are a secondary effect from fungal diseases. • Can also result from insect infestation or environmental or mechanical damage.

Root Rot
Root decay usually caused by fungi favored by overwatering, root damage, drought stress or poor soil conditions. • Affected plants often wilt, even with ample soil moisture, and display dieback and leaf discoloration.
Photos
Image 5114037: Raymond Gill, California Department of Food and Agriculture, Bugwood.org Image 1487040: Sturgis McKeever, Georgia Southern University, Bugwood.org Image 5439081: Joseph Berger, Bugwood.org Image 1476101: Whitney Cranshaw, Colorado State University, Bugwood.org Image 5361242: Frank Peairs, Colorado State University, Bugwood.org Image 5366800: Whitney Cranshaw, Colorado State University, Bugwood.org Image 1572341: Gerald Holmes, Valent USA Corporation, Bugwood.org Image 5388315: William Fountain, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org Image 1427010: Joseph O'Brien,
